Vietnam’s Solar Energy Market: A Comprehensive Outlook for Investors
Vietnam’s solar energy market, driven by high solar potential and strong government support, plays a key role in the country’s “Net Zero” commitment, among other fields of green energy. For foreign investors, this presents a golden opportunity to tap into a rapidly growing sector with sustainable impacts.
Vietnam, a country significantly impacted by climate change, is making substantial strides towards enhancing its resilience and achieving sustainable growth. With a bold commitment to reach “Net Zero” emissions by 2050, the energy sector is pivotal in this transformation. The solar energy market stands out as a rapidly expanding field among the various green energy initiatives. In 2023, renewable energy contributed 13.6 percent of Vietnam’s total electricity production and imports, amounting to 37.9 million kilowatts per hour (kWh). Solar energy was the leading source within this sector, generating 25.7 million kWh and accounting for 9.2 percent. It was followed by wind energy, which produced 11.4 million kWh (4.1 percent), and biomass, which generated 853 million kWh (0.3 percent).
Vietnam’s strategic focus on solar energy not only addresses environmental concerns but also supports the nation’s economic development and energy security. This article explores the dynamic growth of Vietnam’s solar energy development, highlighting industry trends and prospects.
Industry overview
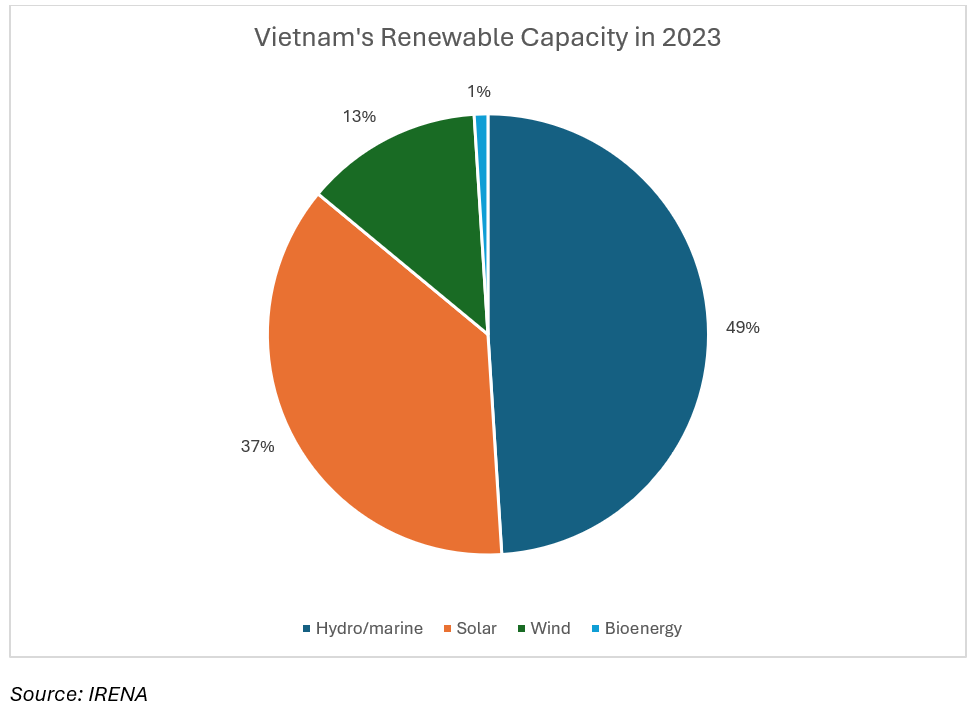
According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the installed solar power capacity, which is the maximum capacity that a solar system is designed to run at in Vietnam, accounts for more than a third of Vietnam’s total renewable energy capacity at 18,854 GW in 2023.
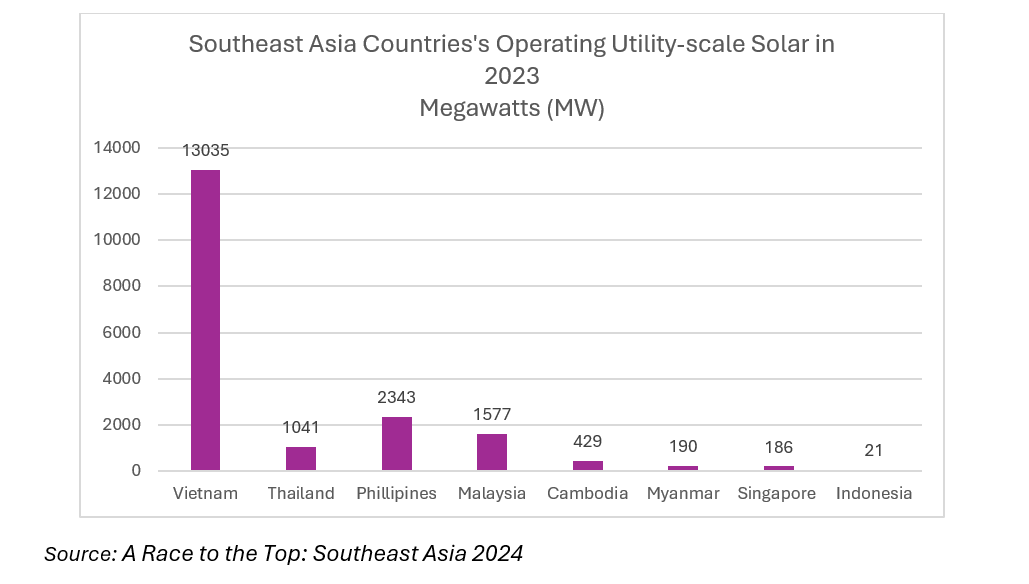
Since 2017, Vietnam has deployed a series of competitive and incentivized investment policies to bring utility-scale solar projects into operation, leading to a boom in solar development. Vietnam is the current regional leader in terms of operating utility-scale solar capacity, with more than double the capacity of the other member countries combined. This number is driven by favorable government policies and substantial private-sector investment.
Recently, the Vietnam government marked a new phase of renewable energy growth with the implementation of Vietnam’s Eighth National Power Development Plan (PDP 8), which is expected to phase out coal power generation by 2050 and increase solar power capacity.
Under PDP 8, solar power is projected to reach 20,591 MW by 2030 and 189,000 MW by 2050, generating 252–291 billion kWh annually. By 2050, solar power is expected to become Vietnam’s largest electricity source, accounting for over 38.5 percent of the nation’s total power capacity. This ambitious plan shows the vital role of private sector participation in driving the energy transition and advancing renewable energy’s share in Vietnam’s power system.
Solar energy growth factors in Vietnam
Geographical location and climate
Vietnam is in the tropical and subtropical climate zones, which provides significant geographic advantages, including a long coastline, a tropical climate, and strong solar irradiance throughout the year. Most provinces and cities in the country benefit from high levels of daily sunlight. Solar radiation in Vietnam ranges from 1,600 to 2,500 hours of sunshine annually, with an average daily radiation of about 230 to 250 kcal/cm. There are no noticeable variations in radiation levels between provinces from year to year, creating a stable environment and a substantial market for the construction of solar energy systems throughout the country.
Demand for electricity
As Vietnam’s economy continues to grow, the demand for electricity—both for consumption and production—is also increasing. In the first nine months of 2024, the total electricity production and import in Vietnam reached 232.6 billion kWh, marking a 10.9 percent rise compared to the same period in 2023. Mordor Intelligence, a market research and advisory firm, projects that Vietnam’s energy demand will increase by 10 percent annually over the next five years, which means the required power capacity will also need to double. Consequently, the solar power market will be crucial in addressing this substantial energy demand.
Supportive policies for Vietnam’s solar energy market
In recent years, the Vietnamese government has implemented an intensive energy strategy that has created new investment opportunities, especially for solar power. Moving forward, the PDP 8 will be the backbone of Vietnam’s energy sector, supported by a robust framework for solar energy initiatives.
- Feed-in Tariff (FiT): This mechanism promotes renewable energy development by making these energy sources more competitive with traditional power generation. Initially, the government offered fixed FiT rates to encourage investment in renewable energy, which provoked critical feedback from across the nation. In response, the government gradually reduced the FiT rate and shifted towards a self-consumption model encouraging on-site power usage. It is incentivized by long-term fixed-price power purchase agreements between individual generators and renewable energy power investors, such as large-energy consumed businesses and Vietnam Electricity (EVN), with obligations and guaranteed access to the grid.
- Regulation on self-production and self-consumption of rooftop solar power: To encourage renewable energy use and minimize environmental impact, the Government of Vietnam issued Decree No. 135/2024/ND-CP on October 22, 2024. This decree facilitates the development of self-production and self-consumption rooftop solar power by reducing barriers such as licensing and construction requirements.
- Trading mechanism: Vietnam has established a trading mechanism for solar energy, allowing both rooftop and large-scale renewable energy generating units to enter direct power purchase agreements (DPPAs) with large electricity consumers. This mechanism was introduced in Decree No. 80/2024/ND-CP in July 2024.
- Other duty exemptions: Solar developers benefit from a corporate income tax exemption for the first four years, a 50 percent reduction for the next nine years, and a 10 percent reduction until the 15th year. Additionally, imported equipment in the solar sector is exempt from tariffs, which lowers technology costs and attracts foreign investment.
With these transformative policies and mechanisms designed to ease and attract private investment, Vietnam is poised for a strong transition toward a more sustainable energy future.
The market outlook for foreign investors
Given solar power’s integration with the national electricity grid, Vietnam’s solar market has become an attractive destination for foreign investment, particularly in the solar panel manufacturing industry. Investors have recognized the country’s commitment to renewable energy, ambitious government targets, relatively flexible terms, and supportive policies for easing project financing. These factors present lucrative growth opportunities.
Vietnam currently has approximately 103,000 rooftop solar power projects across residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, boasting a total installed capacity of over 9,500 MW. By 2030, Vietnam aims to significantly increase its solar capacity, projecting that 50 percent of households will have rooftop solar installations. Specifically, Ho Chi Minh City plans to invest 650 billion VND to install rooftop solar systems in 440 public offices, with a total capacity of more than 43 MW. Consequently, Vietnam actively seeks cooperation with foreign investors and developers, especially those with expertise in photovoltaic (PV) modules, energy storage, and sun-tracking technology.
Conclusion
Vietnam is leading ASEAN countries in terms of total installed renewable energy capacity and related projects. The country is addressing its energy market with plans to enable households to generate their own electricity and export surplus power through solar systems. This shift towards green energy has proven to be a promising development path, resulting in significant growth in power capacity and allied industrial sectors over the past five years.
Vietnam possesses favorable natural geography, strong market demand, and supportive policies that attract investors to solar energy projects. Given these developments and a forward-looking approach, the solar power sector is expected to capture the largest market share in Vietnam over the next five years.
About Us
Vietnam Briefing is published by Asia Briefing, a subsidiary of Dezan Shira & Associates. We produce material for foreign investors throughout Asia, including ASEAN, China, and India. For editorial matters, contact us here and for a complimentary subscription to our products, please click here. For assistance with investments into Vietnam, please contact us at vietnam@dezshira.com or visit us at www.dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates assists foreign investors throughout Asia from offices across the world, including in Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, and Da Nang. We also maintain offices or have alliance partners assisting foreign investors in China, Hong Kong SAR, Dubai (UAE), Indonesia, Singapore, Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh, Italy, Germany, the United States, and Australia.
- Previous Article Vietnamese New Year (Tet) 2025: How to Prepare Your Business
- Next Article Overtime Regulations and Compensation in Vietnam