Due Diligence in Vietnam: Commercial and IT Aspects in the M&A Process
- Due Diligence is a key component in the Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) process in Vietnam giving investors a complete picture of a company before entering into a proposed transaction.
- Euromonitor International rated Vietnam as the world’s second M&A attractive market among 50 economies.
- Apart from legal and financial due diligence, Vietnam Briefing looks at commercial and IT due diligence, which can help investors minimize risk and gain sustainable value through an M&A transaction.
Despite COVID-19, Vietnam remains an attractive M&A market due to its business landscape and now because of its well-controlled pandemic efforts. Most recently, Euromonitor International ranked Vietnam as the world’s second M&A attractive market out of 50 economies. The ranking reflects the expected level of investment, activity, and attractiveness in the global M&A market.
After our previous article on legal and financial due diligence, we look at commercial and IT due diligence, which form the basis of a due diligence during an M&A for most investors.
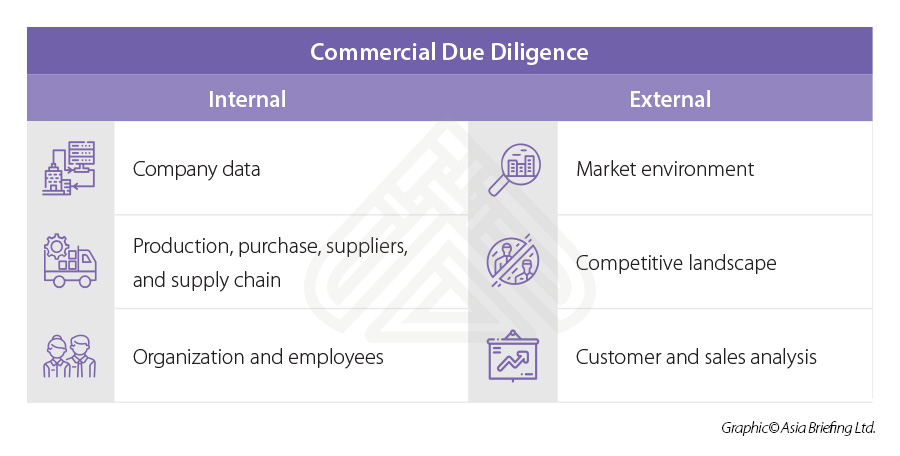
Commercial due diligence
Commercial due diligence looks at aspects of the target company’s market positioning and market share including growth drivers and future prospects. It is a step by step process that determines the overall value from an M&A of a target company.
This aspect is crucial and is often done along with legal and financial due diligence.
Commercial due diligence can look at the following aspects:
Company data
This aspect looks at the company’s key products and services and how its revenues and profits are defined. It also analyzes at the target company’s core strategies and structure, as well as its unique selling proposition (USP).
Production, purchase, suppliers, and supply chain
With Vietnam’s growing as a manufacturing base in Asia and several exporters moving operations from China – this is a significant factor. This aspect looks at the target company’s production capacity, how many factories it operates, and whether its production facilities can meet future demand. Supplier and distributor contracts should also be examined including the credit period given by the supplier.
Such factors will help in providing a detailed analysis of how well the company is operating in regard to production and supply, as ultimately this will determine revenue and investment.
Organization and employees
This aspect looks at the quality of the target company’s workforce. Investors should examine the current incentives offered to employees, turnover rates, severance, and succession policies to see if these need to be changed after the merger or acquisition has finalized. The aforementioned factors help assess the internal environment of the target company.
Market environment
The market environment refers to the industry the target company operates in, as this defines its future growth aspects. This will differ from industry to industry such as IT to airline industry, or footwear. Analyzing the market environment may involve the market size and growth rates, market structure, current market trends, or if it is a buyer or a seller’s market.
Competitive landscape
The competitive landscape looks at the commercial due diligence process at the microeconomic level. This examines key competitors, and the strategies needed to overcome them.
Customer and sales analysis
This is an important aspect and is directly related to profits. During analysis, the buyer may delve into gaining an in-depth understanding of the business-to-business (B2B) or business-to-consumer (B2C) model of the target company. It may also look at the target company’s credit policies and what are their debt management policies. This can then provide a realistic overview of the company’s standing and whether the M&A deal will bring value to the company.
IT Due diligence
Undertaking IT due diligence helps to identify key capabilities, risks, and costs that may have an impact on the company’s value and investment. This type of due diligence looks at the operation or the financial risks of the target company in relation to its IT environment. The buyer may also look at the current IT operating costs and any future growth and expenses.
Variations in the level of IT infrastructure between the target and acquiring company can cause risks in integration and potential future operations. Therefore, it is vital to evaluate core IT systems such as ERP, CRM, and supply chain management to ensure the entities are aligned.
The key elements that need to be included in the due diligence process are:
- Software;
- Hardware;
- Cyber and network security;
- IT support staff;
- Internet and telecommunications network;
- Initiate and plan IT due diligence;
- Risk discovery;
- Risks assessment and analysis;
- IT due diligence report;
Hardware
This includes desktops, laptops, servers, storage devices, printers, mainframe computers, etc. Investors should understand who owns the equipment and how much is it worth. Will there be a need to upgrade and how reliable the equipment is.
Cyber and network security
It is important to gauge the vulnerability of the target company to a cyber-attack. Data encryption programs, network firewalls, the security of online payments, policy on acceptable use of hardware and software, etc.
IT Support
Assess the company’s technical support group, the number of IT staff employed, and their individual roles, training programs. Assess if further training is required.
Internet and telecommunications network
Examine the target company’s current internet and telecommunications set up and see if it will help identify how the company’s computer systems are organized, as well as the preferred methods of communications between employees and customers.
Initiate and plan IT due diligence
In this phase – the buyer checks the strategic goals and project vision of the M&A transaction.
Risk discovery and training
A request is tailored and developed for the target company. Items requested should include IT personnel and organization, tools, applications, IT infrastructure, controls, and governance. This is typically done through data requests and onsite visits.
Risk assessment and analysis
This phase looks at a complete risk assessment based on any operational shortcomings with may impact the M&A process or post-deal integration. If possible, there should be mitigation procedures along with any costs that maybe be incurred.
IT due diligence report
In this final phase, key findings and recommendations should be developed and should tie back to the goals of the deal. It should provide a summary of the target company and should be written in a language understood by non-IT professionals.
About Us
Vietnam Briefing is produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The firm assists foreign investors throughout Asia from offices across the world, including in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. Readers may write to vietnam@dezshira.com for more support on doing business in Vietnam.
- Previous Article Produktionsverlagerung nach Vietnam für US-Unternehmen: Was Sie wissen müssen
- Next Article Mergers and Acquisitions in Vietnam: An Introduction to Key Guidelines and Processes